“Patch Tuesday” is an unofficial term referring to the second Tuesday of each month, when vendors including Microsoft, Adobe, SAP and Google coordinate the release of vulnerabilities in (and patches for) their software products on a fixed cycle. Critical security updates are occasionally released outside of the normal Patch Tuesday cycle, but these are known as “out-of-band” releases.
In this blog post we’ll summarise the key Microsoft Security Updates for the month, but you can access the raw list in full directly at https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide/releaseNote/2025-Jan
There were advisories of several notable exploitations of Microsoft products over the course of the las month, including most prominently yet another NTLM Capture-Replay Attack vulnerability, this time in MS Outlook (CVE-2023-23397). Due to a lack of cryptographic salting, NTLM hashes are “password-equivalent”, meaning that they can essentially be submitted as credentials to other services if captured by attackers. This ability to leverage onward compromise of further systems makes them a highly lucrative and recurring target for attackers.
CISA also reported on the active exploitation of a flaw in the Microsoft’s Kernel Streaming Driver in Windows (CVE-2024-35250) that delivers attackers with privilege escalation to system level access on compromised hosts. Details of the flaw were originally published by a research team competing at the ‘Pwn2Own’ competition in Vancouver 2024, but with POC exploit code being released shortly afterwards it didn’t take long for real-world exploitations to occur.
Finally, following the release of exploit code for a flaw in the Windows LDAP service (CVE-2024-49113) at the beginning of January, reports are now circulating of the active exploitation of the flaw, causing widespread disruption via denial of service (DoS) attacks.
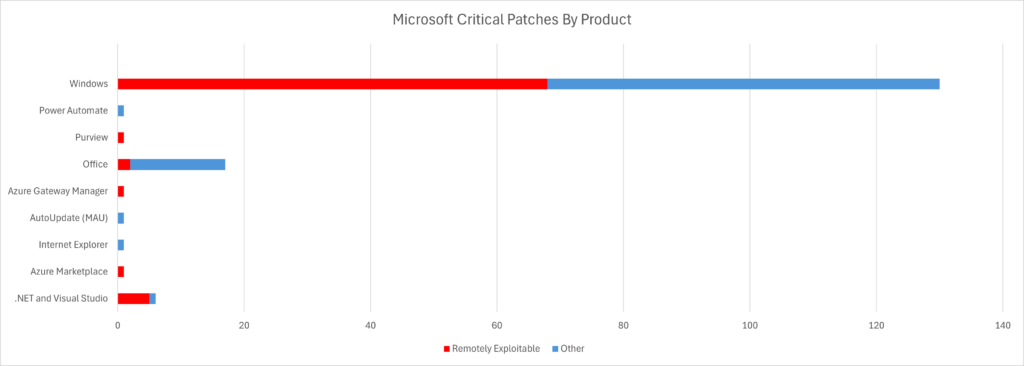
In addition to these widely-covered “known exploitations”, the Microsoft Patch Tuesday update for January 2025 also includes important updates to patch vulnerabilities in products including .NET, Visual Studio, Azure Marketplace, Internet Explorer, Office, Excel, Access, OneNote, Outlook, SharePoint, Word, Windows BitLocker, Windows Boot Manager, Windows Digital Media, and many more!
The list of “Known Exploited” vulnerabilities below represent the greatest risk and absolute highest priority for patching for many organisations. They have been reported by the CISA, America’s Cyber Defense Agency, to be known to be currently being exploited in the wild and at scale, meaning that not only is exploit code known to attackers, but that the weakness is being actively targeted. These vulnerabilities are the most time-critical to patch before being exploited by threat actors.
The AppCheck Scanner is able to detect these vulnerabilities and report on their presence in your technical estate, enabling you to effectively and swiftly target them for remediation – please click each CVE below to read more about each entry on our public-facing Detections database.
| Product | CVE | CVSS Score |
|---|---|---|
| Microsoft Windows – Privilege Escalation via Heap-Based Buffer Overflow in Hyper-V Component | CVE-2025-21333 | 7.8 |
| Microsoft Windows – Privilege Escalation via ‘Use After Free’ Memory Access Violation in Hyper-V Component | CVE-2025-21334 | 7.8 |
| Microsoft Windows – Privilege Escalation via ‘Use After Free’ Memory Access Violation in Hyper-V Component | CVE-2025-21335 | 7.8 |
The list of “Critical” vulnerabilities below are all those with a “CVSS” (Common Vulnerability Scoring System) score of 9.0 or greater. This generally reflects a vulnerability that is a critical risk – being both trivial to exploit as well as having the potential to have significant impact (harm) if successfully exploited – but for which no hard evidence has been gathered yet as to ongoing exploitation. Critical vulnerabilities are crucial to patch, but may be slightly less time-sensitive than ‘known exploited’ vulnerabilities. Critical vulnerabilities highlighted by Microsoft this month include:
| Product | CVE | CVSS Score |
|---|---|---|
| Microsoft Windows (OLE) – Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | CVE-2025-21298 | 9.8 |
| Microsoft Windows (RMCAST) – Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | CVE-2025-21307 | 9.8 |
| Microsoft Windows (NTLM) – Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | CVE-2025-21311 | 9.8 |
The list of “Highly Exploitable” vulnerabilities below are all those which Microsoft has determined are relatively trivial to exploit. Unlike the ‘known exploited vulnerabilities’ list above, there is no evidence yet released of these vulnerabilities having been exploited ‘in the wild’, but that could well change if exploit code is published, or a threat actor chooses to specifically target one of these vulnerabilities. The vulnerabilities flagged as ‘highly exploitable’ by Microsoft this month include:
| Product | CVE | CVSS Score |
|---|---|---|
| Microsoft Windows (Search Service) – Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | CVE-2025-21292 | 8.8 |
| Microsoft Windows (RDS) – Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | CVE-2025-21309 | 8.1 |
| Microsoft Brokering File System – Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | CVE-2025-21315 | 7.8 |
| Microsoft Excel – Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | CVE-2025-21354 | 7.8 |
| Microsoft Excel – Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | CVE-2025-21362 | 7.8 |
| Microsoft Excel – Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability | CVE-2025-21364 | 7.8 |
| Microsoft Office – Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | CVE-2025-21365 | 7.8 |
| Microsoft Windows (Kerberos) – Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability | CVE-2025-21299 | 7.1 |
| Microsoft Windows (SmartScreen) – Spoofing Vulnerability | CVE-2025-21314 | 6.5 |
| Microsoft Windows (MapUrlToZone) – Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability | CVE-2025-21189 | 4.3 |
| Microsoft Windows (MapUrlToZone) – Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability | CVE-2025-21219 | 4.3 |
| Microsoft Windows (MapUrlToZone) – Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability | CVE-2025-21268 | 4.3 |
| Microsoft Windows (HTML Platforms) – Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability | CVE-2025-21269 | 4.3 |
| Microsoft Windows (MapUrlToZone) – Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability | CVE-2025-21328 | 4.3 |
| Microsoft Windows (MapUrlToZone) – Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability | VE-2025-21329 | 4.3 |
| Microsoft Windows (BitLocker) – Information Disclosure Vulnerability | CVE-2025-21210 | 4.2 |
In addition to the above, Microsoft released 159 important security patches in total.
Products affected by this Patch Tuesday’s updates include:
Total Microsoft CVEs: 159
Known Actively Exploited: 3
Critical: 3
Highly Exploitable: 16
Other vendors releasing critical security updates this Patch Tuesday include:
As with every month, if you don’t want to wait for your system to download Microsoft critical updates on pre-determined schedule, you can download them immediately from the Windows Update Catalog website at https://www.catalog.update.microsoft.com/Home.aspx and searching by Microsoft KB ID.
We also recommend scanning your entire estate using the AppCheck vulnerability scanner regularly – including end-user machines running desktop operating systems. Contact your account manager now if you are not already licensed for internal scan hubs to cover your whole estate.
The next MICROSOFT Patch Tuesday update will be on 11th February 2025 – add it to your calendar now!
We also now provide coverage of other critical vulnerability updates from key vendors, including:
AppCheck is a software security vendor based in the UK, offering a leading security scanning platform that automates the discovery of security flaws within organisations websites, applications, network, and cloud infrastructure. AppCheck are authorized by the Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) Program as a CVE Numbering Authority (CNA).
No software to download or install.
Contact us or call us 0113 887 8380
AppCheck is a software security vendor based in the UK, offering a leading security scanning platform that automates the discovery of security flaws within organisations websites, applications, network and cloud infrastructure. AppCheck are authorised by the Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) Program as a CVE Numbering Authority (CNA)







