Last week there was a lot of discussion around CVE-2020-11651 & CVE-2020-11652 – two critical vulnerabilities in SaltStack.
These CVE’s are now being actively exploited in the wild and so we have created a free standalone scanner to detect and report on these.
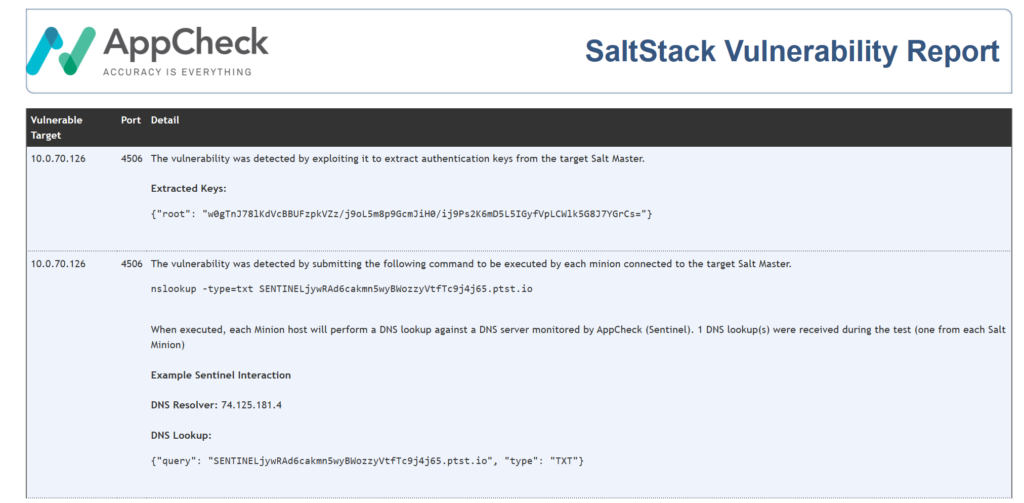
This tool uses two safe exploit techniques to identify (both optional); Root Token extraction and Out-of-Band code execution via AppCheck Sentinel*.
It’s multi-threaded, has html output and can scan entire network range or single host.
The tool is free to use and you don’t need an AppCheck licence to access.
You can download the tool below:
The security researchers responsible for uncovering these vulnerabilities estimate that more than 6,000 vulnerable Salt instances are exposed so be sure to give your environment a scan.
SaltStack released an update [3000.2] in response to the vulnerabilities and if you haven’t already updated, it is strongly recommended to do so.
It is also advised to restrict access to salt master ports (4506) to known minions and block the wider internet until a more robust solution is produced.
Background
Traditionally, web application security flaws are detected by modifying client supplied input in an attempt to trigger a specific response from the server. For example, SQL Injection flaws are often detected by submitting payloads that cause a signature to be returned by the database server, in other cases, payloads are designed to trigger a specific time delay that can be measured to detect the flaw. In each case, these methods use in-band techniques where both the attack and response take the same path as regular website traffic and result in immediate confirmation of the vulnerability.
Out-of-Band Detection
There are cases however where in-band techniques are not effective. For example, consider an e-commerce site that collects orders which are then later reviewed via a back-end order processing system. Whilst AppCheck will detect vulnerabilities (in-band) within the eCommerce site during a routine scan, vulnerabilities within the back-end order processing system may not trigger until they are accessed (by another user or process) later down the line. Other common cases arise when triggering the vulnerability does not provide a reliable in-band mechanism to confirm the flaw. For example, measuring server response times could be unreliable if the normal server response times are erratic. In other cases the vulnerability may not impact the way the server responds regardless of whether it is successfully exploited or not.
In order to overcome these restrictions, AppCheck implements an Out-of-Band detection system named Sentinel.
Sentinel is a Cloud based monitoring system that hosts specially designed DNS, SMTP, HTTP(s) and SMB services that intercept Out-of-band connections triggered as a result of an AppCheck attack payload. During a scan, AppCheck submits specially crafted payloads designed to trigger Out-of-Band connections when they are successfully executed. Sentinel then detects this execution and updates scan results accordingly. One of the most common techniques is the use of DNS tokens embedded within the payload. By design, DNS queries are forwarded to the authoritative DNS server for a given domain in order to be resolved. Therefore, even if the vulnerable system is not permitted to access the internet, as long as it is able to resolve DNS names it can communicate with Sentinel.
If you would like any further information on the tool, or would like to see what other vulnerabilities AppCheck can pick up in our free scan then please get in touch: info@localhost
No software to download or install.
Contact us or call us 0113 887 8380
AppCheck is a software security vendor based in the UK, offering a leading security scanning platform that automates the discovery of security flaws within organisations websites, applications, network and cloud infrastructure. AppCheck are authorised by the Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) Program as a CVE Numbering Authority (CNA)







